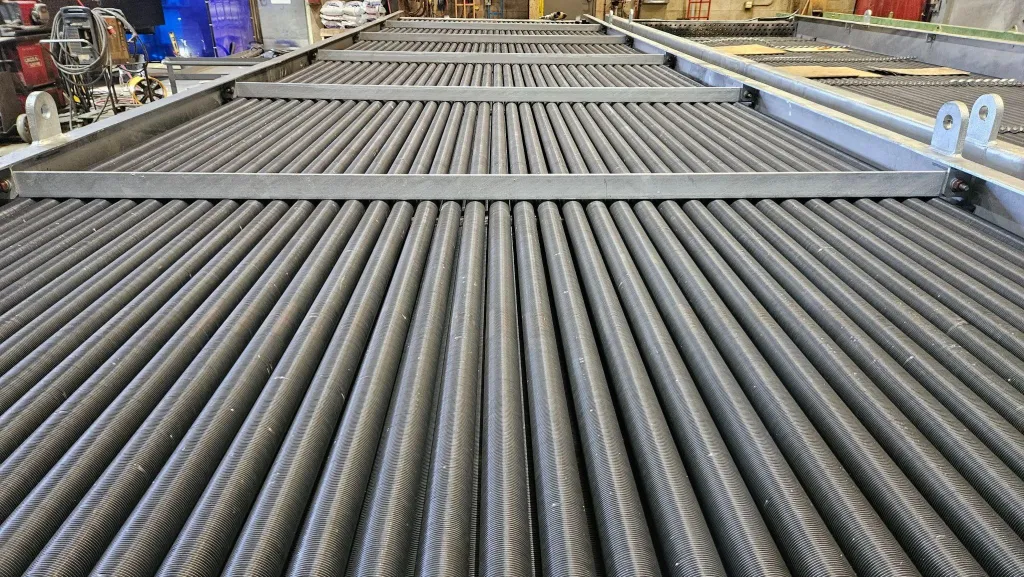
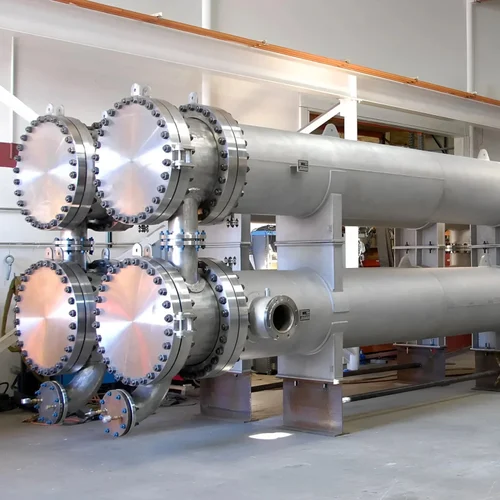
Selecting the appropriate tubular heat exchanger is a critical step for ensuring optimal thermal efficiency, mechanical integrity, and long-term operational reliability. As a widely used heat transfer device in process engineering, tubular designs—especially shell-and-tube heat exchangers—are the preferred choice for a wide variety of industrial applications.
This article outlines the technical and commercial criteria for selecting a tubular heat exchanger and provides guidance on material selection, design parameters, and applicable industry standards.
What Is a Tubular Heat Exchanger?
A tubular heat exchanger, more commonly referred to as a shell and tube heat exchanger, is a type of heat exchanger defined on Wikipedia as a system used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. The shell-and-tube configuration consists of one set of fluid flowing through tubes and another fluid flowing over the tubes within an enclosed shell.
This design is particularly suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to its robust construction and flexibility in thermal performance.
For an engineering-level introduction, see The Engineering Toolbox – Heat Exchangers.
Application-Oriented Selection Guide
Industrial processes vary widely in operating conditions and media characteristics. A successful heat exchanger design requires careful alignment with each application’s unique technical demands.
| Industry | Typical Requirements | Recommended Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | High pressure, corrosive fluids, sour gas | Duplex/super duplex tubes, API 660 standard design |
| Chemical Processing | High temperatures, aggressive acids/solvents | 904L, Hastelloy or titanium materials, multi-pass design |
| Food & Beverage | Sanitary compliance, CIP cleaning, hygienic finish | 316L polished tubes, 3-A Sanitary Standards |
| HVAC Systems | Heat recovery, compact size, cost efficiency | Copper tube bundles, carbon steel shells |
| Power Generation | Thermal cycling resistance, fatigue control | U-tube bundles, expansion joints, high-alloy construction |
More application cases can be found at AZoM – Heat Exchangers in Industry
Material Selection and Corrosion Resistance
Material selection is one of the most important factors influencing the longevity and maintenance cost of heat exchangers. The most commonly used materials include:
- 316L / 304L Stainless Steel – Excellent general corrosion resistance
- Duplex & Super Duplex Stainless Steel – High strength and excellent resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
- Copper-Nickel Alloys (Cu-Ni 70/30) – High thermal conductivity, suitable for seawater service
- Titanium – Outstanding corrosion resistance in saltwater and aggressive chemical environments
- Nickel Alloys (Hastelloy, Inconel) – Effective against high-temperature oxidation and acidic environments
Explore the metallurgical background on Wikipedia – Stainless steel
Key Design Considerations
When designing or procuring a tubular heat exchanger, the following factors must be evaluated:
- Thermal Duty – Define heat load based on process data
- Operating Pressure & Temperature – Select tube and shell materials and wall thickness accordingly
- Fouling Tendency – Impacts material choice and cleaning strategy
- Tube Layout and Pass Configuration – Single-pass, multi-pass, or U-tube
- Compliance Standards – ASME Section VIII, TEMA types, PED (EU Pressure Equipment Directive)
DLSS Solutions for Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
At DLSS – Zhejiang Daling Special Steel Co., Ltd., we supply tailored stainless steel tubing solutions for shell-and-tube heat exchangers in demanding global applications.
Our capabilities include:
- Seamless U-tubes and straight tubes in 316L, 304L, Duplex, and special alloys
- Lengths up to 22 meters, tight OD/WT tolerances
- High-precision polishing (Ra ≤ 0.4 μm) for hygienic or high-purity applications
- Support for EN 10216-5, ASTM A213, ASME, PED, and GB/T certifications
- Non-destructive testing, hydro test, eddy current, PMI, and 100% dimensional inspection
We serve over 40 countries in energy, chemical, food processing, marine, and HVAC sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are shell-and-tube heat exchangers suitable for vacuum and high-pressure applications?
Yes. Their design allows them to operate under extreme pressure conditions. For further reference, see Wikipedia – Pressure vessel.
Q2: Can tubular heat exchangers be designed for phase change (condensation or evaporation)?
Yes. Their versatility makes them well-suited for condensing steam or evaporating process fluids.
Q3: What cleaning methods are recommended?
Options include mechanical pigging, chemical CIP (clean-in-place), or manual rod cleaning depending on the design and fluid type.
Q4: What documentation is typically provided?
Standard documentation includes tube data sheets, mill test certificates (EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2), compliance declarations (ASME, PED), drawings, and inspection reports.
Contact Us
For technical support, quotations, or project consultations:
Email: info@dlsspipe.com
Website: https://www.dlsspipeline.com
Our engineering and commercial teams are here to support your global heat exchanger projects.