Meta Description:
Understand the differences between 304L, 316L, and 904L stainless steel tubes. Learn how to choose the right material based on corrosion resistance, cost, and application requirements.
Introduction
Stainless steel tube buyers often face the challenge of selecting the most suitable grade for their projects. Among the most widely specified austenitic stainless steels are:
- 304L – General-purpose stainless tube
- 316L – Enhanced corrosion resistance in chloride environments
- 904L – Premium alloy for aggressive chemicals and seawater
Each material offers unique strengths, costs, and applications. In this blog, we break down the chemical, mechanical, and practical differences to help engineers and procurement teams make the right decision.
1. Chemical Composition Comparison
| Element (%) | 304L | 316L | 904L |
|---|---|---|---|
| C (max) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Cr | 18.0 – 20.0 | 16.0 – 18.0 | 19.5 – 23.5 |
| Ni | 8.0 – 12.0 | 10.0 – 14.0 | 23.5 – 28.5 |
| Mo | — | 2.0 – 3.0 | 4.0 – 5.0 |
| Cu | — | — | 1.0 – 2.0 |
| PREN (est.) | ~19 | ~24 | ~35+ |
Key Insight: 904L contains high levels of nickel and molybdenum, giving it exceptional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Reference: Outokumpu Stainless Datasheets
2. Corrosion Resistance: Which One Holds Up Best?
- 304L: Adequate in general indoor, mildly corrosive, or food environments
- 316L: Preferred for coastal, chemical plant, and heat exchanger applications
- 904L: Performs well in sulfuric acid, seawater, and aggressive chloride media
Use Case Examples:
- 304L: Furniture tubing, dairy pipelines, water tanks
- 316L: Heat exchanger tubes in food/pharma plants, condensers
- 904L: Desalination units, offshore platforms, acid leaching lines
Key Keywords: 904L seawater tubing, 316L heat exchanger pipe, 304L stainless tube corrosion
3. Mechanical Properties
| Property | 304L | 316L | 904L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (MPa) | ~205 | ~205 | ~220 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ~515 | ~515 | ~530 |
| Elongation (%) | ≥ 40 | ≥ 40 | ≥ 35 |
| Hardness (HRB, max) | 90 | 95 | 90 |
904L has slightly higher strength and maintains ductility despite higher alloying content.
4. Weldability & Fabrication
- 304L & 316L: Easily welded with standard fillers like ER308L, ER316L
- 904L: Requires low heat input and specialized fillers like ER385
- Bending and cutting of 904L may require more effort due to increased strength and work hardening rate
Pro Tip: For U-bend heat exchanger tubes, 316L is the easiest to form, while 904L may require larger bending radii.
5. Cost Considerations
| Grade | Relative Cost | Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 304L | $$ | Most economical, widely available |
| 316L | $$$ | Higher Mo and Ni content |
| 904L | $$$$+ | Premium alloy with high nickel/molybdenum |
904L’s high alloy content makes it significantly more expensive. However, in extreme environments, the cost is justified by reduced maintenance and replacement cycles.
6. Which One Should You Choose?
| Requirement | Recommended Grade |
|---|---|
| General corrosion resistance | 304L |
| Moderate chloride exposure | 316L |
| High chloride or sulfuric acid | 904L |
| Budget-sensitive project | 304L |
| Long-term offshore reliability | 904L |
Conclusion
Choosing between 304L, 316L, and 904L stainless steel tubes depends on your project’s corrosion environment, mechanical demands, and budget. While 304L remains cost-effective, 316L provides better protection in corrosive zones, and 904L stands out in the most aggressive chemical applications.
DLSS Tube Capabilities
- ASTM A213 / A269 / B677 seamless tubes in 304L, 316L, 904L
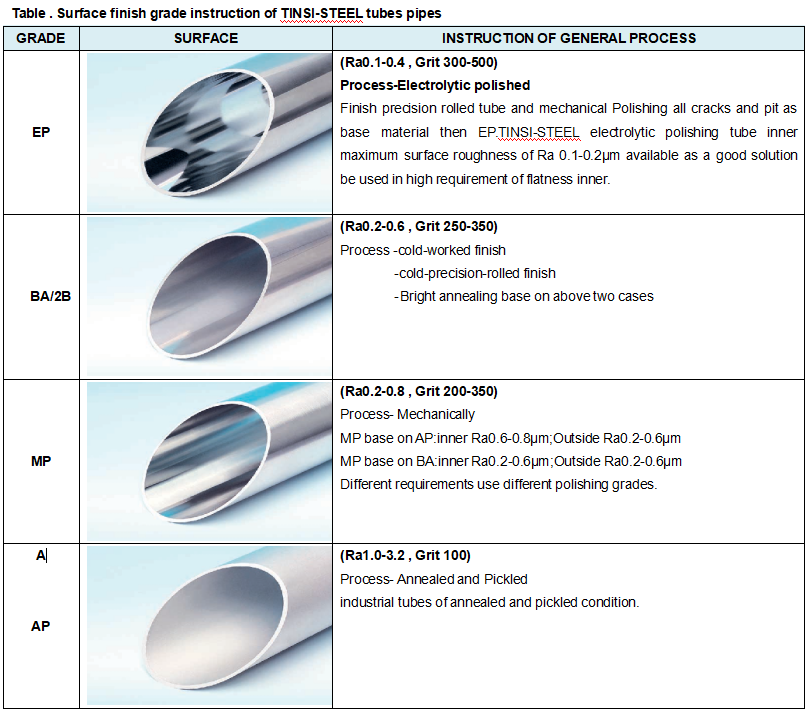
- U-bend, BA, pickled, or polished surface
- 100% Eddy Current and Hydro Test
- 3.1/3.2 MTC with PMI, hardness, grain size reports
- Packaging: export wooden crates, seaworthy wrapping
Contact DLSS
Email: info@dlsspipe.com
Website: www.dlsspipeline.com
Need help selecting the right stainless grade for your tubes? Contact our technical team today for free material consultation and quotations.