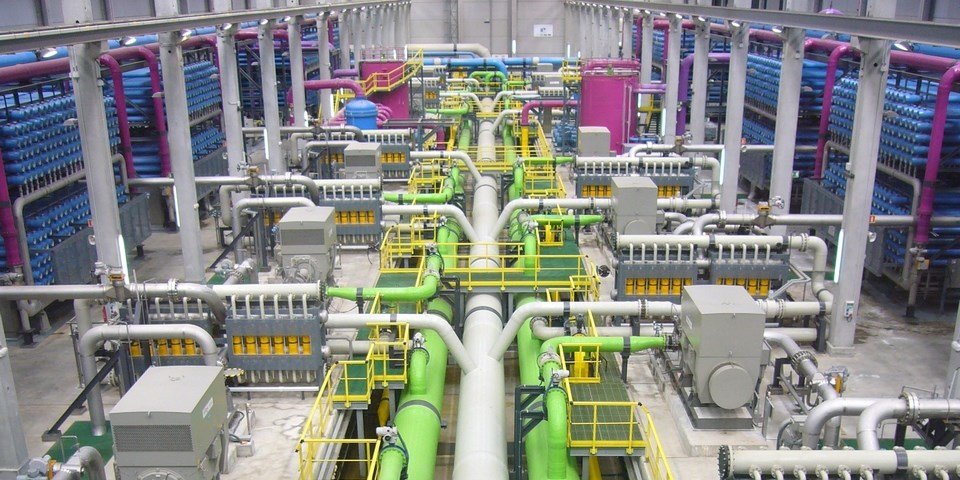
In the food and pharmaceutical industries, cleanliness is not optional—it’s mandatory. Heat exchangers in these sectors are integral to pasteurization, sterilization, CIP (clean-in-place) loops, and product temperature control.
That’s why the choice of tubing is critical. Sanitary-grade stainless steel tubes ensure both product safety and regulatory compliance, while also withstanding the harsh cleaning agents and high-frequency thermal cycles these systems endure.
1. What Makes a Tube “Hygienic”?
Hygienic tubes differ from standard industrial stainless steel tubes in the following ways:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Surface finish | Polished or bright annealed with Ra ≤ 0.4–0.8 µm ID (internal diameter) |
| Weld quality | Orbital welded or seamless, free from pits and crevices |
| Cleanability | Compatible with CIP, SIP (steam-in-place), and aggressive cleaners |
| Traceability | Full batch traceability with EN 10204 3.1 MTC |
| Certifications | Meet ASTM A270, ASME BPE, or EN 10357 standards |
Tubes must be non-reactive, non-toxic, and resistant to microbiological growth.

2. Where Tubes Are Used in Food & Pharma Systems
| Application | Tube Role |
|---|---|
| Milk pasteurizers | Transfer heat while preventing contamination between media |
| Bioreactors / fermenters | Maintain process temperature with clean steam or water |
| CIP systems | Rapid flushing of pipes and tanks with caustic solution |
| WFI (Water for Injection) loops | Ultra-pure, low-carbon TP316L piping |
| Syrup, sauce, vaccine production | Tube-in-tube or shell-and-tube heat exchange with hygienic seals |
Even small flaws—like weld beads or scale residues—can harbor bacteria and lead to product recall, contamination, or regulatory violations.
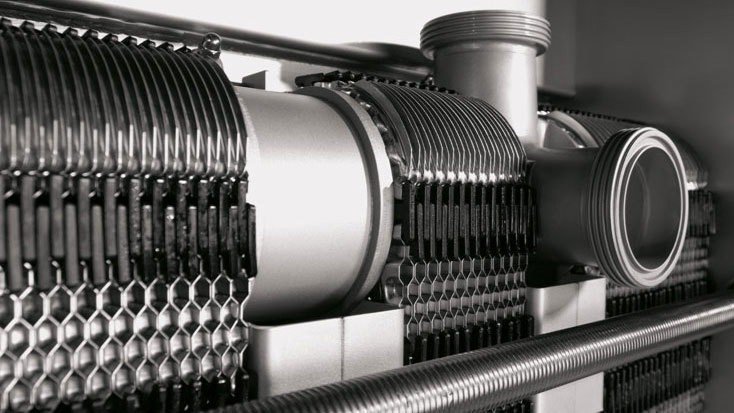

3. Common Tube Grades and Standards
| Grade | Standard | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| TP316L | ASTM A270 / A269 | Dairy, brewery, bio-pharma |
| TP304 / 304L | ASTM A249 / EN10357 | Beverages, food-grade steam |
| EP Tubes (Electro-Polished) | ASME BPE / ISO 1127 | Biotech and injectable drugs |
| TP316Ti / 904L | For acidic or aggressive environments | Tomato paste, acid-based cleaners |
DLSS produces hygienic stainless steel tubes with automatic polishing, pickling-passivation, and full certification—ideal for system integrators and OEMs in the food/pharma sectors.

4. What OEMs and End Users Expect
| Expectation | DLSS Capability |
|---|---|
| Ra ≤ 0.6 μm ID finish | Bright annealed, polished tubes with test report |
| Seamless or TIG-welded with no crevice | Controlled welding and annealing process |
| Clean packaging | PE bag + end caps + ISO pallet + labeling |
| Documentation | 3.1 MTC, surface roughness report, PMI, welding logs |
| Batch control | Alloy + heat number + project tracking |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between industrial and sanitary stainless steel tubes?
A: Sanitary tubes have smoother surface finishes (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm or lower), higher cleanliness, tighter tolerances, and are tested for cleanability and compatibility with hygienic systems.
Q2: Why is TP316L preferred in pharma and dairy systems?
A: TP316L resists corrosion from chlorides and acidic cleaning agents, and has low carbon content to prevent sensitization during welding.
Q3: What packaging is used for hygienic tubes?
A: Tubes are cleaned, sealed with caps, wrapped in PE or VCI film, bundled in clean wood or plastic pallets, and labeled with alloy, batch, and inspection date.
Q4: Can DLSS provide welding documentation and Ra test reports?
A: Yes. DLSS offers surface roughness tests (per 10–20 pieces per batch), orbital weld QC, and full welding logs on request.
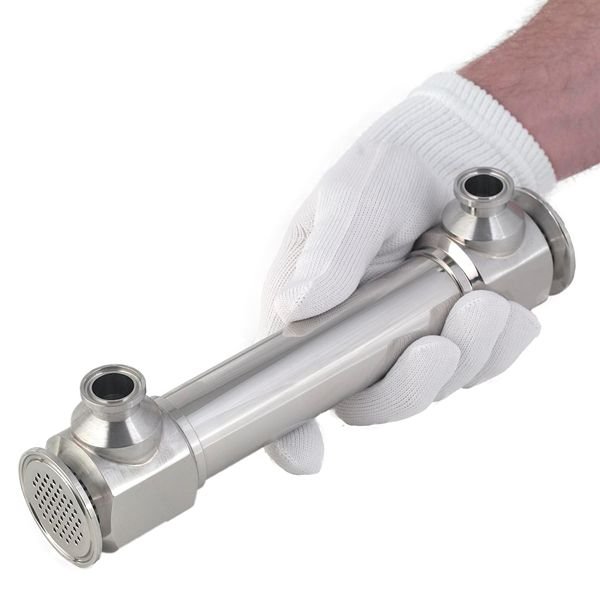

Conclusion: Clean Tubes, Clean Process, Safe Product
In food and pharmaceutical manufacturing, a single tube flaw can shut down production. That’s why hygienic-grade stainless steel tubes must be engineered with precision, cleanliness, and confidence.
DLSS proudly supports global food and pharma clients with sanitary heat exchanger tubing that meets the highest international standards—from dairy to biotech.
Because when it comes to safety, there is no margin for contamination.