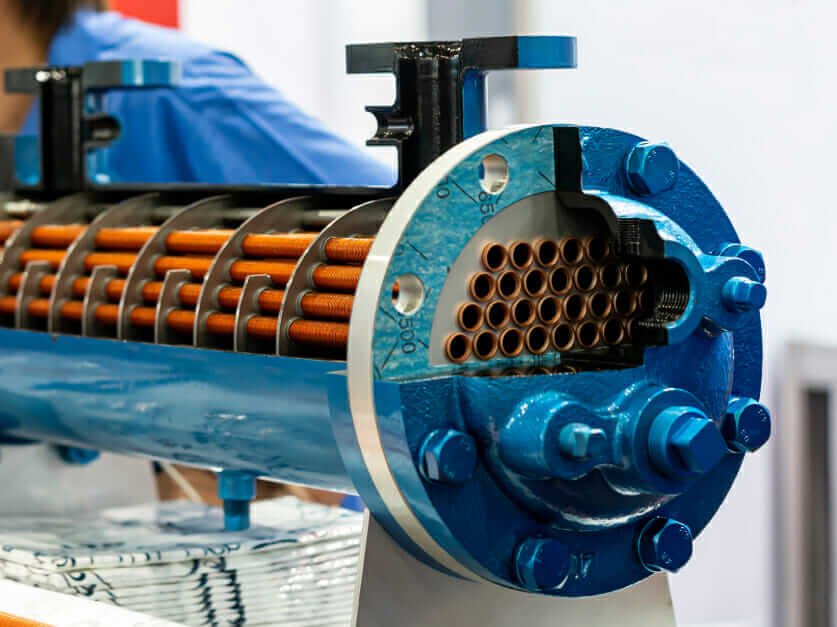
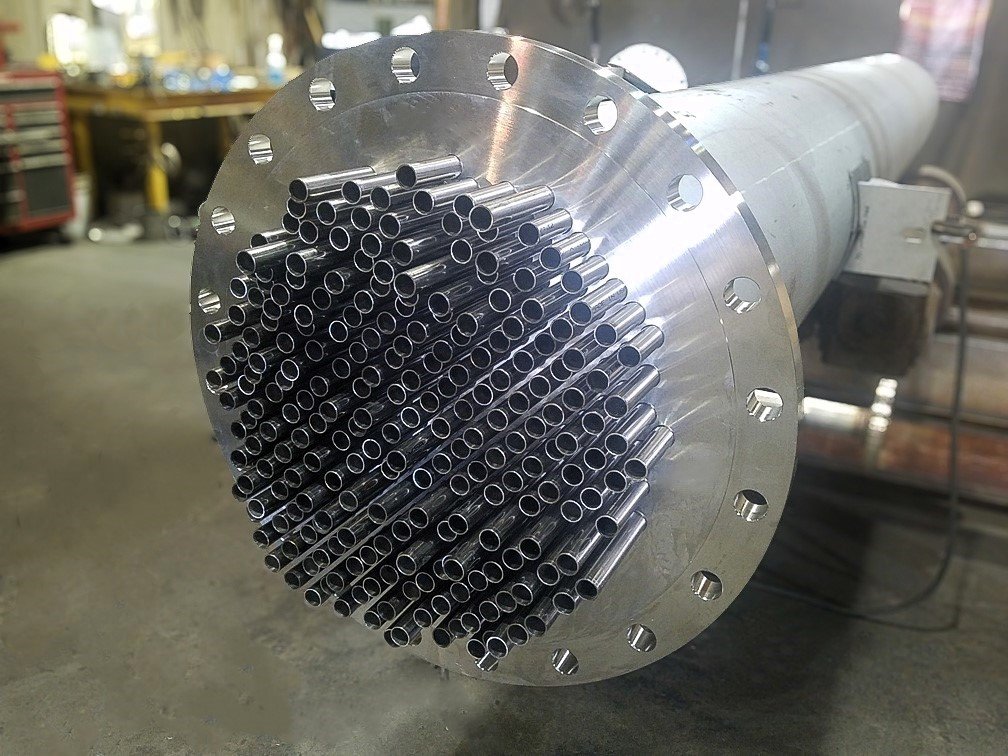
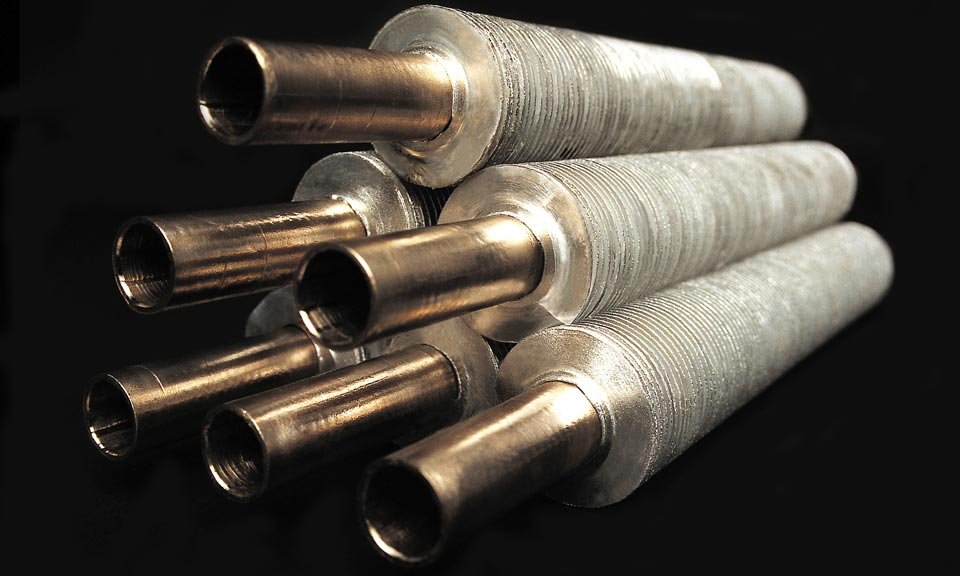
In various industrial and domestic applications, heat exchangers are essential for optimizing thermal efficiency, reducing energy waste, and lowering operational costs. Among the many designs, pipe-based heat exchangers play a crucial role due to their structural simplicity and high effectiveness.
This blog explores four common types: the Double Tube Heat Exchanger, Stove Pipe Heat Exchanger, Exhaust Pipe Heat Exchanger, and Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger—highlighting their working principles, applications, and material requirements.
1. Double Tube Heat Exchanger: Reliable and Modular
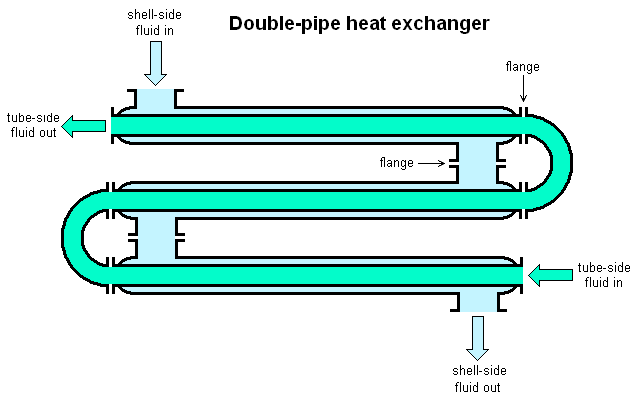
The double tube heat exchanger, also known as the double pipe heat exchanger, is a simple and cost-effective design where two concentric pipes allow heat transfer between fluids. One fluid flows through the inner pipe while the other moves in the annular space between the pipes.
Advantages:
- Ideal for high-temperature differences
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Suitable for modular extension
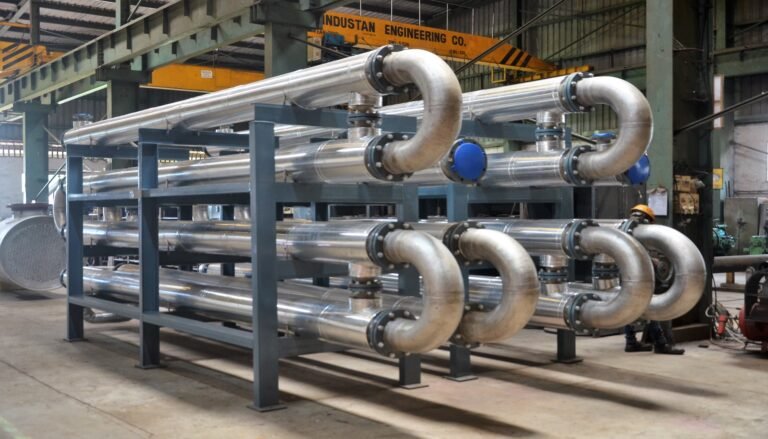

Applications:
- Oil and gas
- Chemical processing
- Cooling lubricants or heating fluids in small batch operations
Learn more about DLSS stainless steel tubing for double tube heat exchanger applications
2. Stove Pipe Heat Exchanger: Maximizing Residential Heating Efficiency
A stove pipe heat exchanger is commonly used in wood stoves or pellet stoves to reclaim waste heat from the stove’s exhaust gases. These systems circulate room air around hot exhaust pipes to improve heating efficiency without consuming extra fuel.
Benefits:
- Enhances energy utilization in homes
- Reduces heating costs
- Simple and affordable installation
Materials:
- Heat-resistant stainless steel pipes (e.g., 304 or 409)
- Galvanized steel with heat coating
3. Exhaust Pipe Heat Exchanger: Waste Heat Recovery in Industry
In power plants, engine systems, or incinerators, exhaust pipe heat exchangers recover heat from high-temperature flue gases. This reclaimed energy is then used to preheat combustion air or water, significantly improving system efficiency.
Key Applications:
- Diesel generators
- Combined heat and power (CHP) systems
- Industrial furnaces
- Marine engines
Design Considerations:
- Corrosion resistance
- High thermal conductivity
- Vibration resistance
DLSS provides seamless stainless steel pipes ideal for exhaust heat exchanger systems.
4. Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger: Passive, High-Efficiency Cooling
The heat pipe heat exchanger uses a sealed tube containing a working fluid that vaporizes and condenses to transfer heat passively. These systems are highly efficient and have no moving parts.
Use Cases:
- Data center cooling
- Electronics thermal management
- Energy recovery in HVAC systems
Why It Works:
- Rapid thermal response
- Minimal maintenance
- No external power required

Material Selection for Pipe-Based Heat Exchangers
When selecting pipes for any heat exchanger application, materials must withstand:
- Thermal stress
- Corrosion (especially in acidic or marine environments)
- Pressure fluctuations
Stainless steel seamless tubes, such as TP316L, TP304, and duplex grades like 2205 or 2507, are ideal for most heat exchanger applications. These materials offer excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and long service life.
Conclusion
From industrial exhaust recovery to household heating systems, pipe-based heat exchangers come in various forms, each optimized for specific functions. Whether you’re engineering a double tube heat exchanger for a chemical plant or integrating a stove pipe heat exchanger into a residential setup, choosing the right design and material is critical for performance and reliability.
Explore our full range of stainless steel tube solutions at www.dlsspipeline.com
Contact us: info@dlsspipe.com









