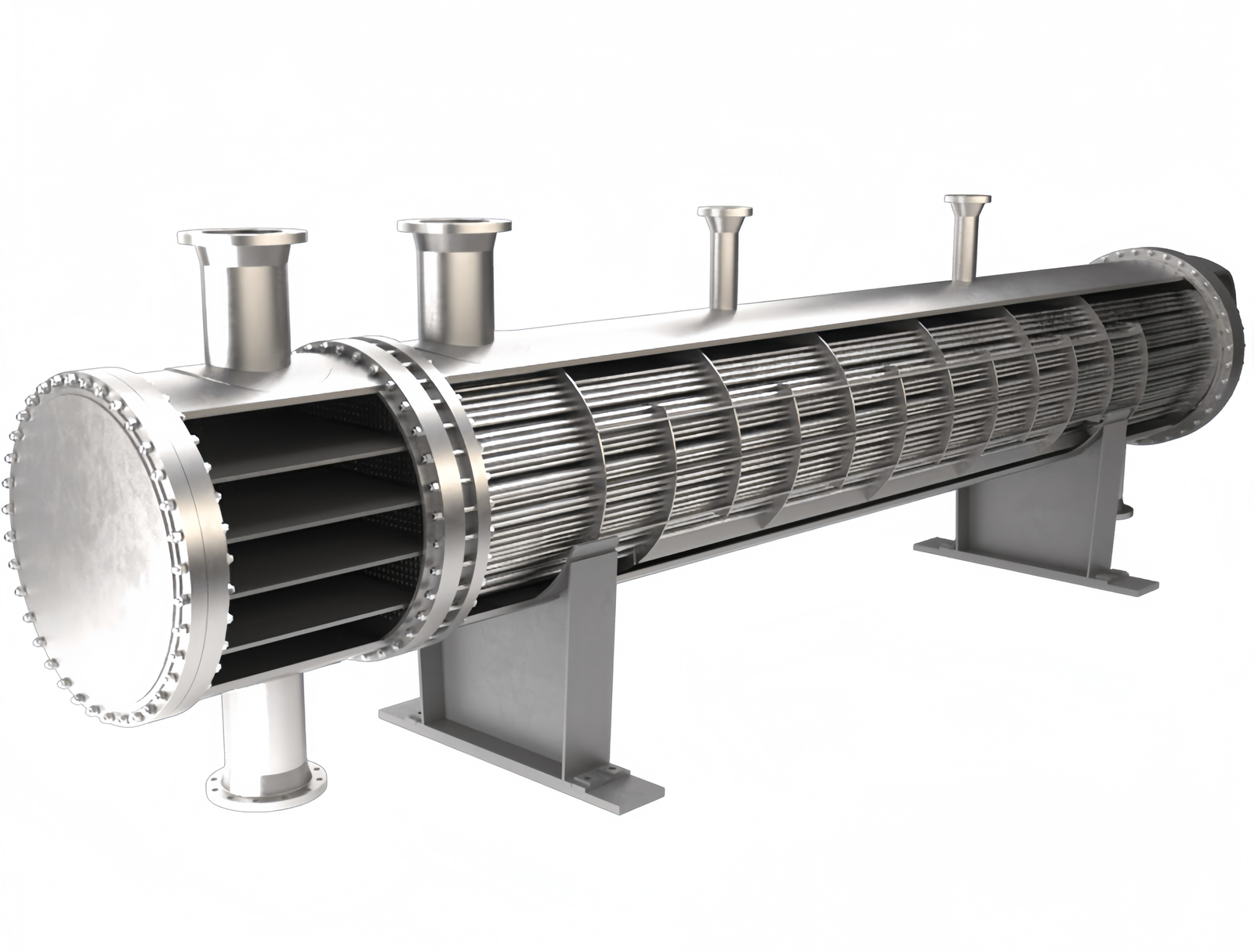
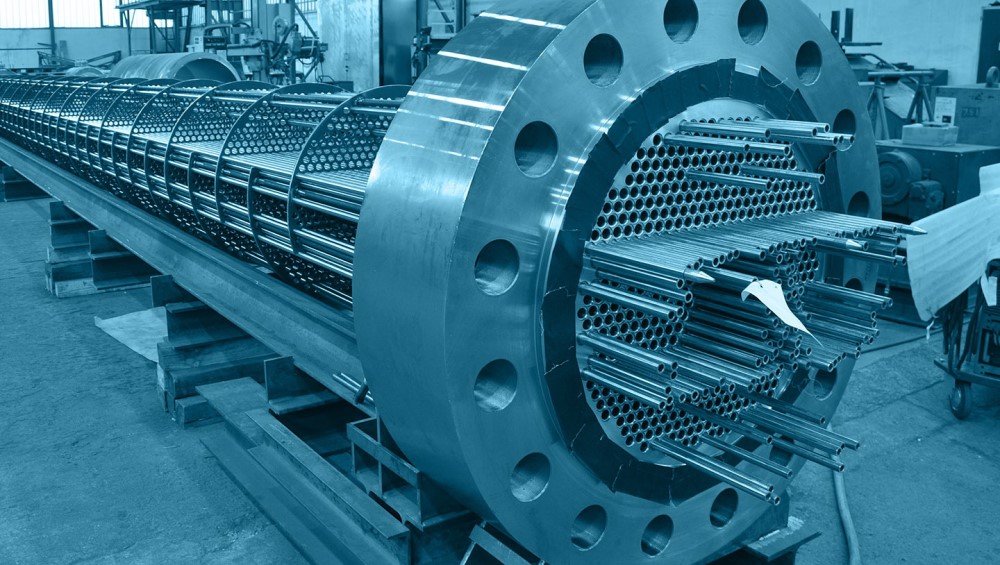
As global interest in renewable energy grows, geothermal systems are increasingly being adopted for heating, cooling, and even power generation. At the heart of these systems are geothermal heat exchangers, responsible for transferring thermal energy between the ground and the working fluid.
This article explains how geothermal heat exchangers work, compares types, discusses key challenges (like corrosion), and shows why stainless steel tubing is a critical component in building long-lasting and efficient systems.
What Is a Geothermal Heat Exchanger?
A geothermal heat exchanger is a system that transfers heat between a fluid (typically water or a glycol mix) and the earth. This process enables buildings to draw warmth in winter and release heat in summer using stable subsurface temperatures.
Common system types include:
- Closed-loop horizontal or vertical systems
- Open-loop systems using groundwater
- Direct-use geothermal systems in high-temperature areas
These systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial HVAC and even in geothermal power plants for energy production.
Types of Geothermal Heat Exchanger Configurations
| System Type | Description | Heat Exchanger Role |
|---|---|---|
| Ground-source heat pump (GSHP) | Transfers heat between buildings and earth via buried loops | Transfers heat from brine or refrigerant to building loop |
| Geothermal district heating | Large-scale systems for urban heating (Europe, China) | Often includes plate/shell-and-tube exchangers |
| Binary geothermal power plant | Uses ground heat to vaporize a secondary fluid (like isobutane) | Stainless shell-and-tube exchanger between water and vapor |
| Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) | Injected water into hot dry rock regions | High-temperature titanium or duplex tube exchangers |
More info: Wikipedia – Geothermal Power
Challenges in Geothermal Heat Exchange
1. Corrosive Groundwater
Many geothermal sources contain chlorides, hydrogen sulfide, CO₂, or minerals that cause corrosion, scaling, and biofouling.
2. Long-Term Durability
Piping and exchangers are expected to operate underground for 25–50 years, often with limited access for maintenance.
3. Thermal Cycling
Frequent heating/cooling cycles require materials with high thermal fatigue resistance.
Why Stainless Steel Tubes Are Essential
DLSS recommends the use of corrosion-resistant stainless steel and titanium tubes in geothermal heat exchanger systems due to:
- High corrosion resistance in aggressive mineral-rich water
- Excellent mechanical strength and long service life
- Weldability and fabrication ease for custom heat exchanger designs
- Compatibility with ASME, EN, and PED codes
- Material traceability and certification
Especially recommended grades:
| Material | Best for |
|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | Shallow ground loop systems with mild chloride levels |
| Duplex 2205 / Super Duplex 2507 | High-chloride, deeper geothermal wells |
| Titanium Gr.2 | Extreme salinity or sulfur-rich geothermal environments |
Explore more: DLSS Stainless and Duplex Tubes for Heat Exchangers
Design Tips for Geothermal Heat Exchangers
- Use seamless stainless tubes for corrosion resistance and pressure containment
- Bright annealed or polished finish reduces fouling and improves flow
- Specify U-bent or multi-pass shell-and-tube designs for high-efficiency recovery
- Use double-tube or double-wall tubes in potable-water applications to prevent cross-contamination
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can geothermal systems use carbon steel tubes to save cost?
No. Carbon steel corrodes rapidly in geothermal fluids. Stainless steel or titanium is highly recommended.
Q2: What are the typical pressure ratings for geothermal exchangers?
Usually from 10 to 35 bar, depending on system depth and configuration.
Q3: Do I need special certifications for geothermal heat exchanger tubes?
Yes. DLSS provides tubes with EN 10204 3.1, ASME, PED, and NACE MR0175 certifications as required.
Q4: How long do geothermal heat exchangers last?
Properly designed and installed systems using stainless steel can last 25–50 years with minimal maintenance.
Contact Us
DLSS helps geothermal developers, EPC contractors, and OEMs build high-efficiency, low-maintenance, and corrosion-resistant heat exchange systems with:
- Seamless stainless, duplex, and titanium tubes
- Custom lengths, U-bends, polishing, and surface treatment
- Full material documentation and export packaging
- Delivery to over 40 countries
Email: info@dlsspipe.com
Website: www.dlsspipeline.com
Let’s build the future of renewable heat—together.