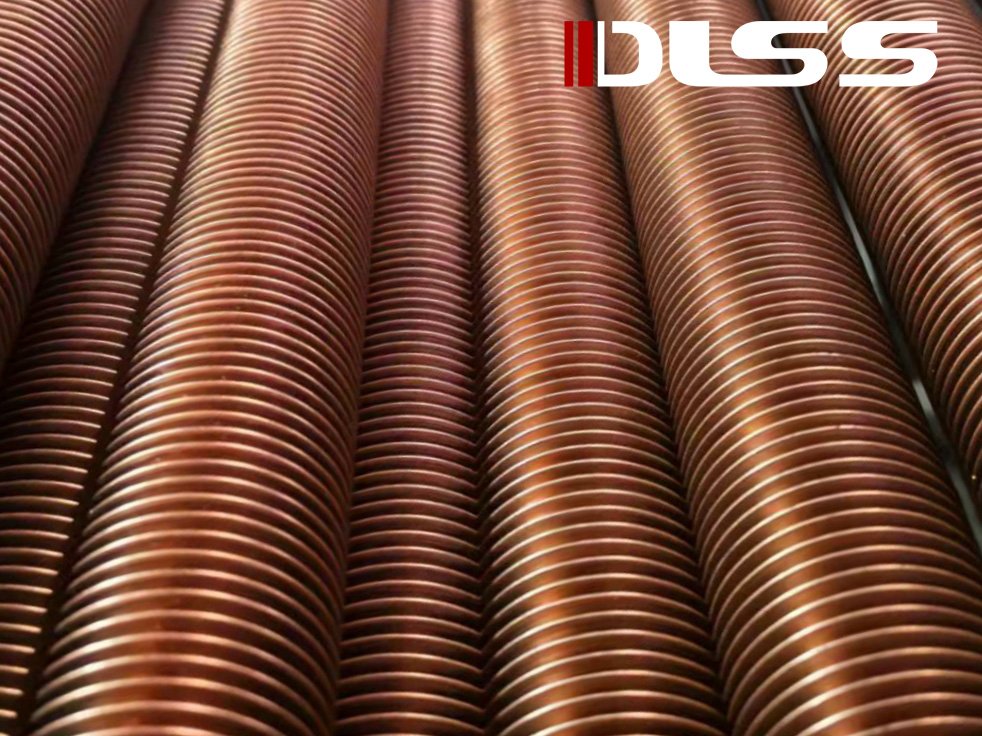
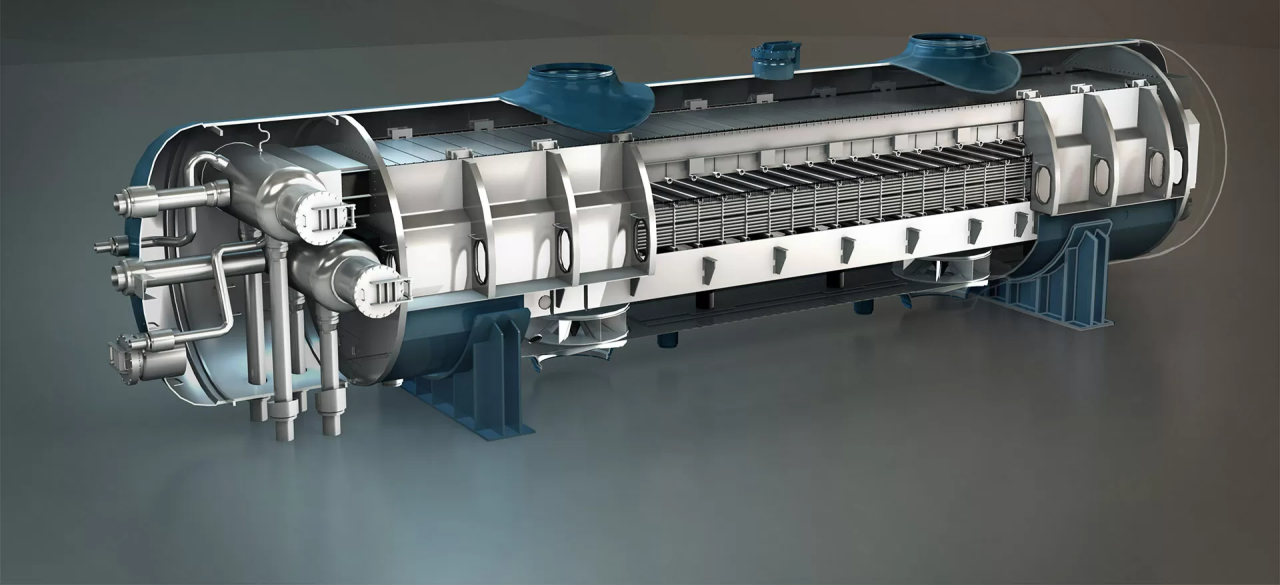
Finned tubes are a specialized type of heat transfer component designed to increase the surface area available for heat exchange between fluids. By adding extended surfaces or “fins” to the tube’s exterior, these components can significantly improve the efficiency of heat exchangers, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, or higher heat transfer performance is required.
How a Finned Tube Works
In a heat exchanger, heat flows from the hot fluid to the cooler fluid across the tube wall. The rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the surface area available. Finned tubes increase this surface area without increasing the overall size of the heat exchanger. This means more heat can be transferred per unit length of tubing, resulting in better efficiency.
For example, in air-cooled heat exchangers, the addition of fins helps transfer heat from the tube wall to the surrounding air more effectively, improving the cooling performance without requiring larger equipment.
Key Benefits of Using Finned Tubes
- Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency – The fins provide additional surface area, allowing faster thermal exchange between fluids.
- Compact Design – Enables high heat transfer rates without increasing the equipment’s footprint.
- Material Flexibility – Finned tubes can be manufactured from stainless steel, carbon steel, copper, titanium, or other alloys, depending on application requirements.
- Cost Savings – Improved efficiency can lead to smaller equipment sizes and lower operating costs.
- Versatility – Suitable for a wide range of industries, including power generation, petrochemical, marine, HVAC, and food processing.
Common Applications
Finned tubes are widely used in:
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers – To improve air-side heat transfer.
- Boilers and Economizers – For recovering waste heat.
- Marine Condensers – In seawater cooling systems.
- HVAC Systems – For heating and cooling in commercial and industrial facilities.
Finned Tube Types and Variations
The performance of a finned tube depends on its design. Some popular types include:
- High-Frequency Welded Finned Tubes – Strong mechanical bond and excellent heat transfer.
- Extruded Finned Tubes – Aluminum fins mechanically bonded to the base tube for superior corrosion resistance.
- Spiral Finned Tubes – Continuous helical fins for large surface area.
- Low-Fin Tubes – Smaller fins rolled into the tube surface for moderate enhancement.
(You can learn more about Different Types of Finned Tubes in our dedicated guide.)
Conclusion
Finned tubes play a critical role in improving heat exchanger efficiency by enhancing heat transfer performance without requiring a larger system. By selecting the right finned tube design and material for your application, you can optimize performance, save energy, and extend equipment life.
At DLSS, we manufacture precision-engineered finned tubes for industrial, marine, and energy applications worldwide. Our solutions are built for durability, efficiency, and long-term performance.
Looking for the right finned tube for your project?
Contact us today via www.dlsspipeline.com or email us at info@dlsspipe.com. Our technical team is ready to help you select the most efficient and cost-effective solution.