1. Introduction – Prevent Fouling in Heat Exchangers
Knowing how to prevent fouling in heat exchangers is essential for maintaining high efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. Fouling occurs when unwanted deposits form on heat transfer surfaces, decreasing thermal performance and increasing operational expenses.
Whether you operate a shell and tube heat exchanger in a chemical plant or a plate heat exchanger in marine applications, fouling prevention is critical for long-term reliability.
For broader performance strategies, read our guide 5 Proven Ways to Improve Heat Exchanger Efficiency.
2. What Is Fouling and Why It Matters
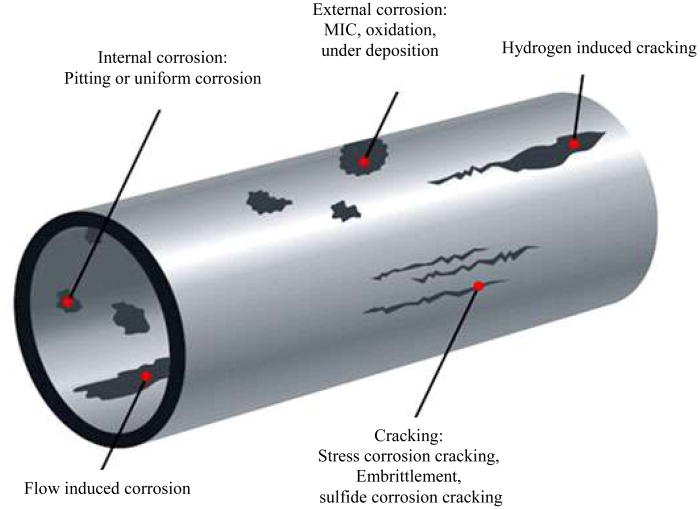
Fouling refers to the accumulation of unwanted materials—such as minerals, biological growth, corrosion products, or particulates—on heat exchanger surfaces.
Common effects of fouling include:
- Reduced heat transfer coefficient
- Increased pressure drop and pumping costs
- Higher energy consumption
- More frequent cleaning and downtime
3. Types of Fouling in Heat Exchangers
- Scaling – Precipitation of minerals such as calcium carbonate from heated water.
- Particulate Deposition – Settling of suspended solids on tube surfaces.
- Biological Fouling – Biofilm formation from microorganisms, algae, or mussels, common in seawater systems.
- Corrosion Product Deposition – Rust or oxides from upstream components.
- Chemical Fouling – Polymerization or other chemical reactions creating solid deposits.
4. 7 Effective Ways to Prevent Fouling in Heat Exchangers
1. Select the Right Materials
Use corrosion-resistant alloys such as stainless steel 316L, duplex stainless 2205, or titanium for aggressive environments. Learn more about our heat exchanger tubes designed for low-fouling applications.
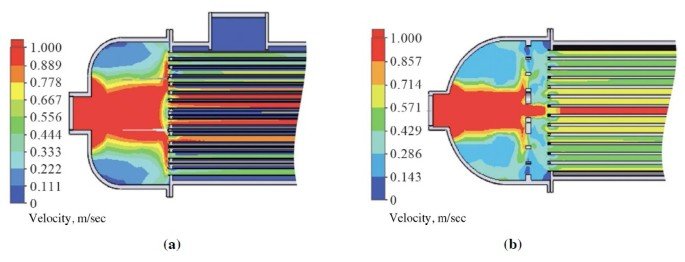
2. Optimize Flow Velocity
Maintain fluid velocity above the fouling threshold to minimize sediment deposition.
3. Use Surface Treatments and Coatings
Anti-fouling coatings, such as PTFE or advanced CVD coatings, can reduce biofilm and scaling adhesion.
4. Implement Water Treatment
Maintain proper pH, hardness, and chemical balance. Remove suspended solids through filtration.
5. Design for Easy Cleaning
Removable tube bundles in shell and tube exchangers allow faster maintenance. Follow TEMA standards for maintenance-friendly designs.
6. Schedule Preventive Maintenance
For broader performance gains, see how to improve heat exchanger efficiency, and keep your PM program tight with this maintenance checklist.
7. Monitor Performance Continuously
Install temperature and pressure sensors to detect early fouling signs and schedule cleaning proactively. See ASME guidelines for maintenance recommendations.
5. Real-World Example
A marine engineering company replaced carbon steel tubes with duplex stainless steel 2205 in their seawater-cooled shell and tube heat exchangers. The upgrade reduced biological fouling by 60% and extended cleaning intervals from 6 months to 18 months, saving significant labor and downtime costs.
6. Conclusion
Preventing fouling in heat exchangers is far more cost-effective than dealing with its consequences. By combining the right materials, proper system design, water treatment, and regular maintenance, you can achieve higher efficiency, lower operating costs, and longer service life.
For corrosion-resistant material selection, see our article Best Material for Seawater Heat Exchanger.
Contact DLSS
At DLSS, we manufacture high-quality stainless steel tubes for heat exchanger applications, ensuring optimal heat transfer, corrosion resistance, and long service life.
Email: info@dlsspipe.com
Website: www.dlsspipeline.com
Related Reading
- 5 Proven Ways to Improve Heat Exchanger Efficiency
- Heat Exchanger Maintenance Checklist
- Heat Exchanger Tube Materials: Pros and Cons