Meta Description:
Understand the key differences between ultrasonic testing (UT) and eddy current testing (ECT) for stainless steel and alloy heat exchanger tubes. Learn which method is best for your application.
Introduction
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is essential in the manufacturing and inspection of stainless steel tubes used in critical heat exchanger systems. Among the most widely used methods are:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT)
But which one is better for your project? The answer depends on material type, tube thickness, surface condition, and defect detection goals.
This article breaks down each method’s principles, pros and cons, and their suitability for different tube inspection needs.
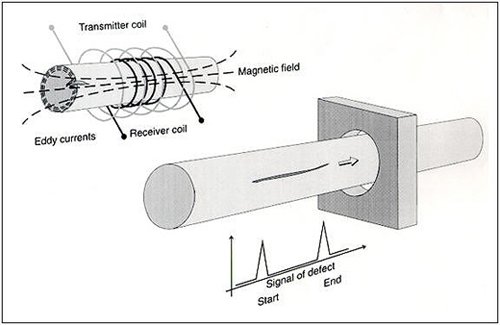
What Is Ultrasonic Testing (UT)?
Ultrasonic testing uses high-frequency sound waves (typically 1–10 MHz) to detect internal defects. A transducer sends sound into the tube wall, and any echo (reflection) reveals anomalies such as:
- Laminations
- Inclusions
- Cracks
- Wall thickness variations
UT Standards for Tubes:
- ASTM E213: UT for seamless metal tubes
- ASME SA-388: UT for forged products
- EN ISO 10893-10: UT of steel tubes for pressure purposes
See official ASTM E213 overview
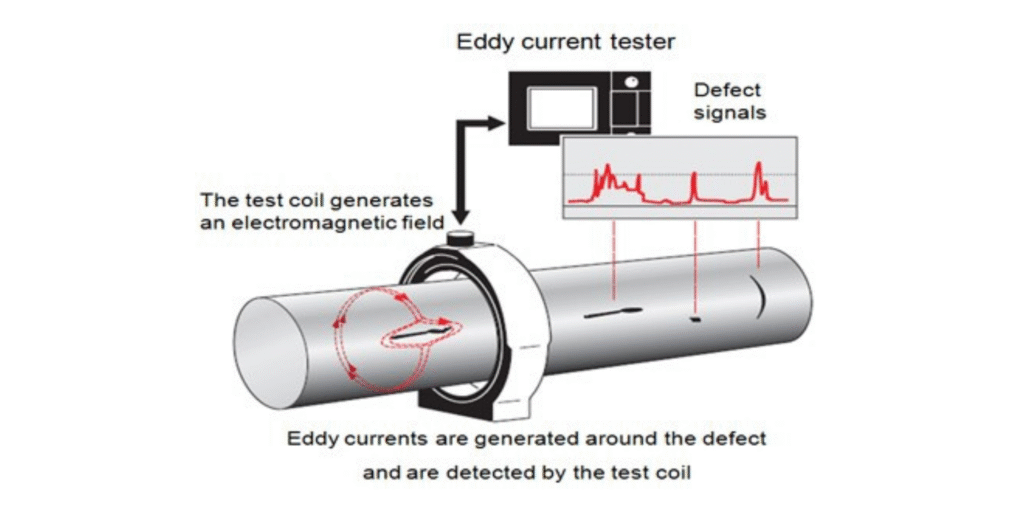
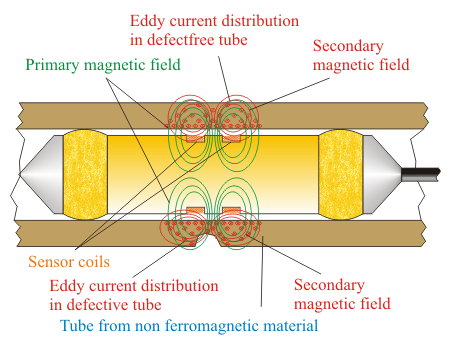
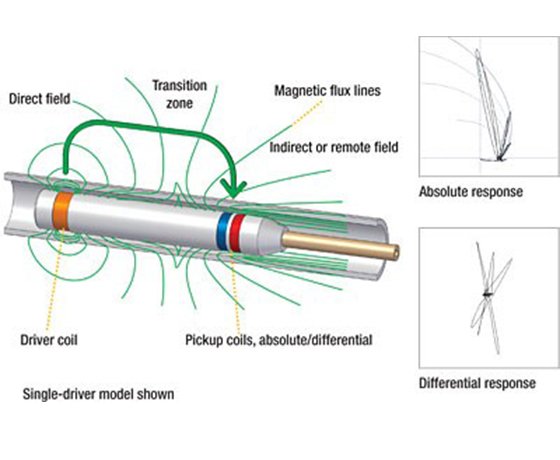
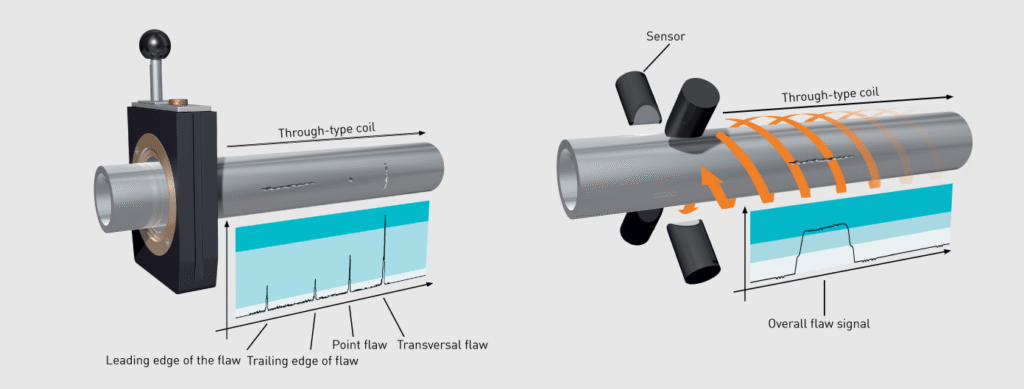
What Is Eddy Current Testing (ECT)?
Eddy current testing works by generating electromagnetic fields in conductive materials. When a probe passes through or around the tube, variations in conductivity or permeability cause distortions, revealing:
- Surface defects
- Subsurface flaws (within 1–2 mm depth)
- Corrosion pitting
- Seam weld defects
ECT is highly effective on non-magnetic stainless steels (like 316L) and thin-wall tubes.
ECT Standards for Tubes:
- ASTM E426: ECT of nonferrous tubes
- EN ISO 10893-2: ECT of seamless and welded steel tubes
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
| Feature | Ultrasonic Testing (UT) | Eddy Current Testing (ECT) |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | High-frequency sound waves | Electromagnetic induction |
| Detects | Internal flaws, wall thickness | Surface and near-surface defects |
| Penetration Depth | Full-wall | 1–2 mm max |
| Surface Prep Needed | Yes (couplant, clean surface) | Minimal |
| Suitable for Magnetic Materials | Yes | No (limited to non-magnetic) |
| Speed | Slower (requires calibration) | Faster (especially for 100% ECT) |
| Ideal For | Weld flaws, laminations, thickness | Surface cracks, ID/OD pitting |
| Common Standards | ASTM E213, ISO 10893-10 | ASTM E426, ISO 10893-2 |
When to Use UT vs ECT in Heat Exchanger Tubes
| Application | Recommended Method | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| High-pressure boiler tubes | UT | Detects wall thickness & deep flaws |
| Non-ferrous condenser tubes (CuNi, Brass) | ECT | Fast and effective for surface pitting |
| Austenitic stainless steel (316L) | ECT + optional UT | Good surface scan; combine if full wall is critical |
| Duplex/super duplex tubes | UT | Better for through-wall inclusions |
| Welded tubes | UT or combination with ECT | Validate weld seam + surface finish |
DLSS Inspection Capabilities
DLSS provides 100% NDT inspection options upon request, including:
- 100% UT for seamless heat exchanger tubes
- 100% ECT for thin-wall or condenser-grade tubes
- Hydrostatic Testing for pressure validation
- Visual + Dimensional Checks as per EN 10216, ASTM A213
All tests are certified in the Mill Test Certificate (MTC) with traceable results and heat numbers.
Real-World Example: Duplex Tube Order for Offshore Platform
A Norwegian client requested 25.4×2.11 mm S32205 duplex tubes for an offshore cooler. Their specification required:
- 100% UT to EN ISO 10893-10
- Wall thickness verification (±0.05 mm)
- Seam weld confirmation via PT (for welded samples)
DLSS successfully delivered the order with zero rejection—verified by third-party TUV inspector onsite.
Conclusion
UT and ECT are complementary tools in stainless steel tube inspection. Depending on your tube grade, wall thickness, and defect sensitivity:
- Use UT for deep defects and structural soundness
- Use ECT for surface flaw detection and fast screening
DLSS supports both methods in-house or via certified third parties, ensuring the integrity of your heat exchanger tubes before shipment.
Contact DLSS for NDT-Qualified Tubes
Email: info@dlsspipe.com
Website: www.dlsspipeline.com
Need help specifying the right inspection method for your project? We’re here to guide you—test by test.









